Un inversor híbrido combina la funcionalidad de un inversor tradicional conectado a la red y un inversor aislado de batería. Le permite conectar sus paneles solares a la red y también almacenar el exceso de energía en baterías para usarla durante períodos de baja generación solar o durante un corte de energía. Los inversores híbridos se utilizan habitualmente en instalaciones solares residenciales y comerciales para aumentar el autoconsumo y la independencia energética.
marca:
SunArk:
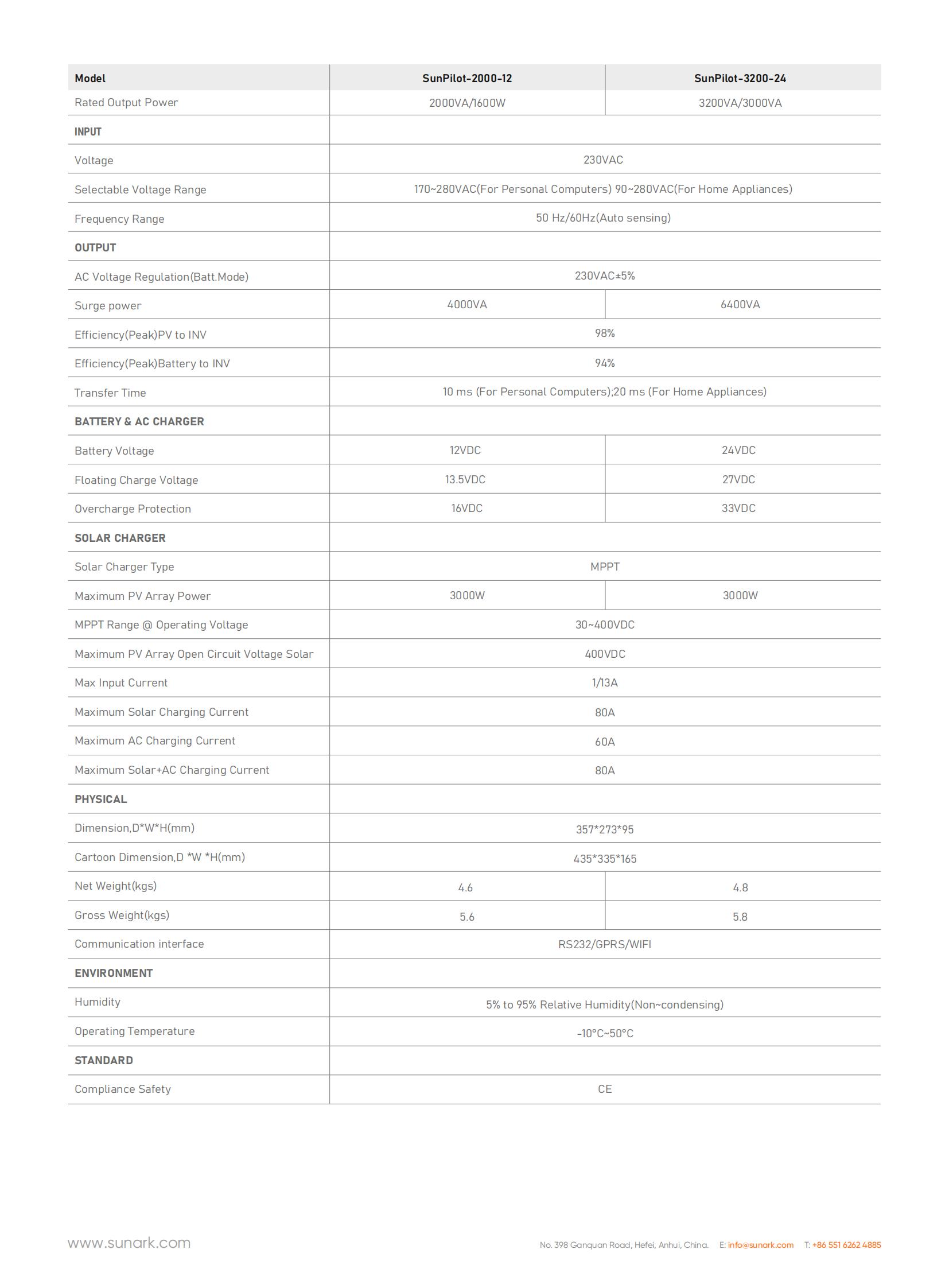
SunArk SunPilot-3200-24 3000W 30~400VDC 3200VA 230VAC±5%La hoja de datos de SunArk SunPilot serie 3200VA se encuentra a continuación:
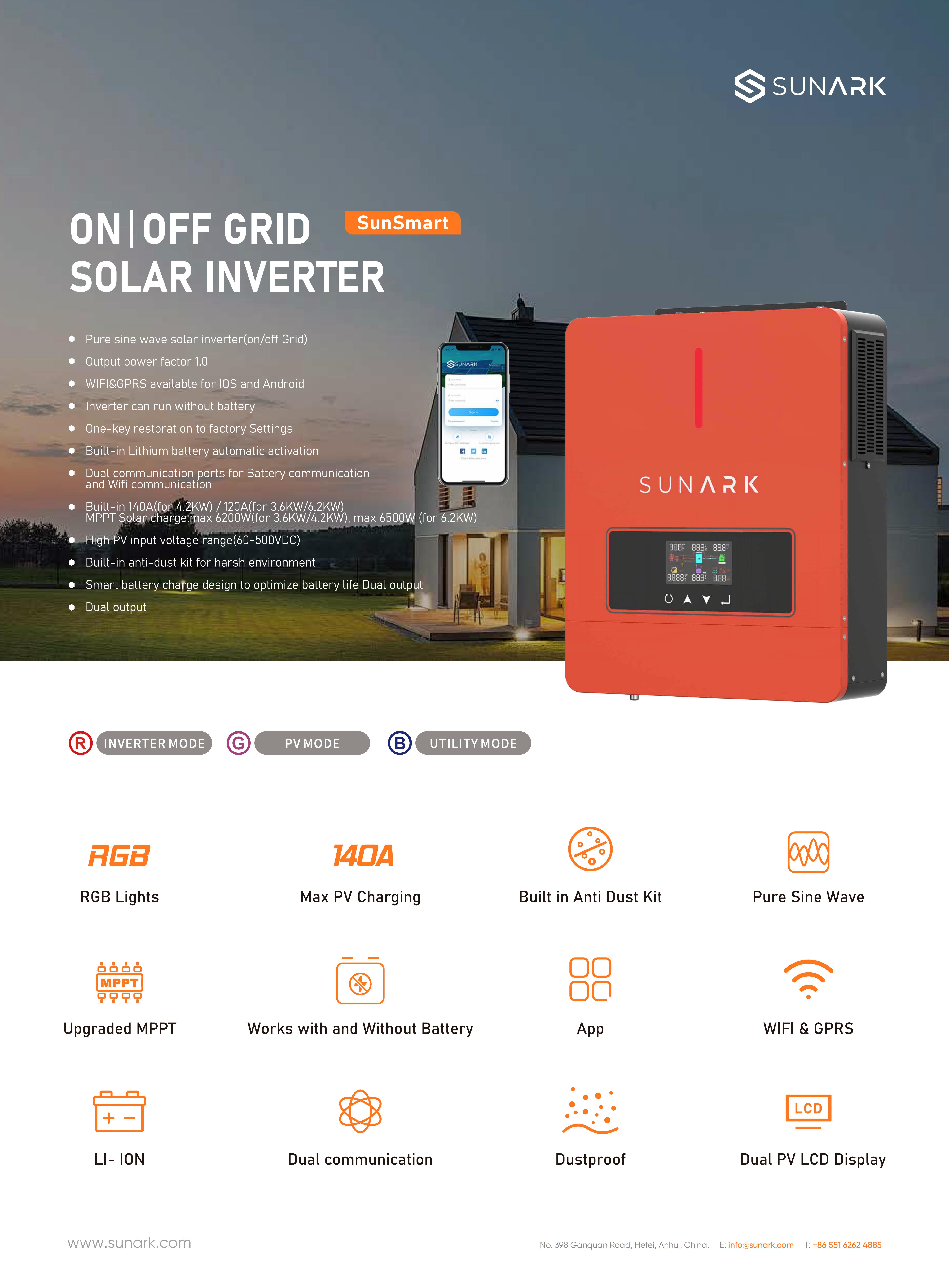
Diferentes colores para elegir:

Un inversor solar híbrido es un tipo avanzado de inversor que combina las funcionalidades de un inversor solar tradicional y un inversor de batería. Su función principal es gestionar y optimizar el flujo de electricidad entre los paneles solares, las baterías y la red eléctrica en un sistema de energía solar híbrido.
Las principales funciones de un inversor solar híbrido incluyen:
Conversión de energía solar: el inversor solar híbrido convierte la electricidad CC (corriente continua) producida por los paneles solares en electricidad CA (corriente alterna) que puede usarse para alimentar electrodomésticos e inyectar a la red eléctrica.
Carga de baterías: en un sistema solar híbrido, el exceso de energía solar que no se consume inmediatamente se almacena en baterías. El inversor híbrido gestiona la carga de las baterías regulando la cantidad de energía de los paneles solares que se destina a cargar las baterías.
Descarga de la batería: cuando se necesita electricidad después del atardecer o durante un corte de energía, el inversor híbrido permite que la energía almacenada en las baterías se convierta nuevamente en electricidad de CA y se utilice para alimentar los electrodomésticos. Cambia sin problemas entre energía de la red, energía de la batería y energía solar según la disponibilidad y la demanda de electricidad.
Interacción con la red y medición neta: en los sistemas solares híbridos, el exceso de energía solar producida durante el día se puede devolver a la red eléctrica y el inversor híbrido gestiona la interacción entre la red y el sistema solar. Permite la medición neta, donde cualquier exceso de electricidad generada se exporta a la red y el propietario recibe créditos o facturas de electricidad reducidas.
Cambio de carga y gestión de energía: el inversor híbrido optimiza el uso de la energía solar y el almacenamiento de la batería en función de diversos factores, como la demanda de energía, la hora del día, el nivel de carga de la batería y las tarifas eléctricas. Gestiona inteligentemente el flujo de electricidad para priorizar el uso de energía solar y energía almacenada siempre que sea posible, reduciendo la dependencia de la electricidad de la red y optimizando el consumo de energía.
Monitoreo y control: los inversores solares híbridos a menudo incluyen funciones de monitoreo y control que permiten a los usuarios monitorear el rendimiento del sistema solar, el estado de la batería, la producción y el consumo de energía. Algunos inversores también ofrecen capacidades de monitoreo y control remoto a través de aplicaciones para teléfonos inteligentes o plataformas en línea.
Overall, the function of a hybrid solar inverter is to efficiently integrate solar power, battery storage, and grid electricity to maximize energy self-consumption, load flexibility, and overall system efficiency in a hybrid solar power system.

In a solar system, a hybrid inverter plays a crucial role in managing the flow of electricity between the solar panels, batteries, and the electrical grid. Here's how a hybrid inverter typically works in a solar system:
Solar Power Conversion: The hybrid inverter receives the DC electricity produced by the solar panels and converts it into usable AC electricity. This process is called inversion. The inverter ensures that the AC electricity generated matches the requirements of the appliances and electrical loads in the house.
Energy Consumption: The hybrid inverter prioritizes the use of solar electricity to power the household appliances and meet the immediate energy demand. It will direct the solar power to the loads within the house, reducing or eliminating the need to draw electricity from the grid.
Battery Charging: If there is excess solar power that is not immediately consumed, the hybrid inverter manages the charging of the batteries. It regulates the amount of energy directed from the solar panels to the batteries to ensure optimal charging without overcharging.
Battery Discharging: When electricity is required at a time when solar energy is not available, such as during nighttime or a power outage, the hybrid inverter draws electricity from the batteries. It converts the DC electricity stored in the batteries back into AC electricity, allowing it to power the household appliances.
Grid Interaction: In a hybrid solar system, the hybrid inverter enables interaction with the electrical grid. If there is surplus solar energy that cannot be immediately consumed or stored in the batteries, the inverter can feed the excess electricity back into the grid. This allows the homeowner to earn credits for the excess energy produced, usually through a net metering arrangement.
Monitoring and Control: Hybrid inverters often include monitoring and control features that provide real-time data on energy production, consumption, battery status, and system performance. Users can monitor their system's performance, adjust settings, and access historical data to optimize energy usage.
Seamless Switching: The hybrid inverter ensures seamless and automatic switching between different power sources. It can monitor the energy availability, prioritize the use of solar power and battery storage, and switch to drawing electricity from the grid when necessary. The transition between power sources is typically smooth and uninterrupted.
En general, el inversor híbrido actúa como el eje central de un sistema solar, gestionando la conversión, el consumo, el almacenamiento y la distribución de electricidad para maximizar la eficiencia energética y la autosuficiencia. Optimiza el uso de la energía solar, aprovecha la energía de la red y carga y descarga las baterías de manera eficiente, proporcionando un suministro de electricidad confiable y rentable para el.